Remedies of Cough

Quelling your cough
The treatment for your cough will be determined by the type of cough and its cause. The best method to manage a cough caused by a viral illness is to let the immune system handle it; such coughs usually go away on their own. A doctor will focus on the source of a cough when treating it.
Management Strategies for Cough
If your cough is linked to a specific medical condition (e.g., asthma, COPD, pulmonary fibrosis, sinus drainage issues, nasal polyps, or GERD), your doctor may prescribe targeted treatments. Keep in mind that chronic cough may not always respond to treatment, known as “chronic refractory cough.” It’s essential to maintain open communication with your provider about any changes in your condition.
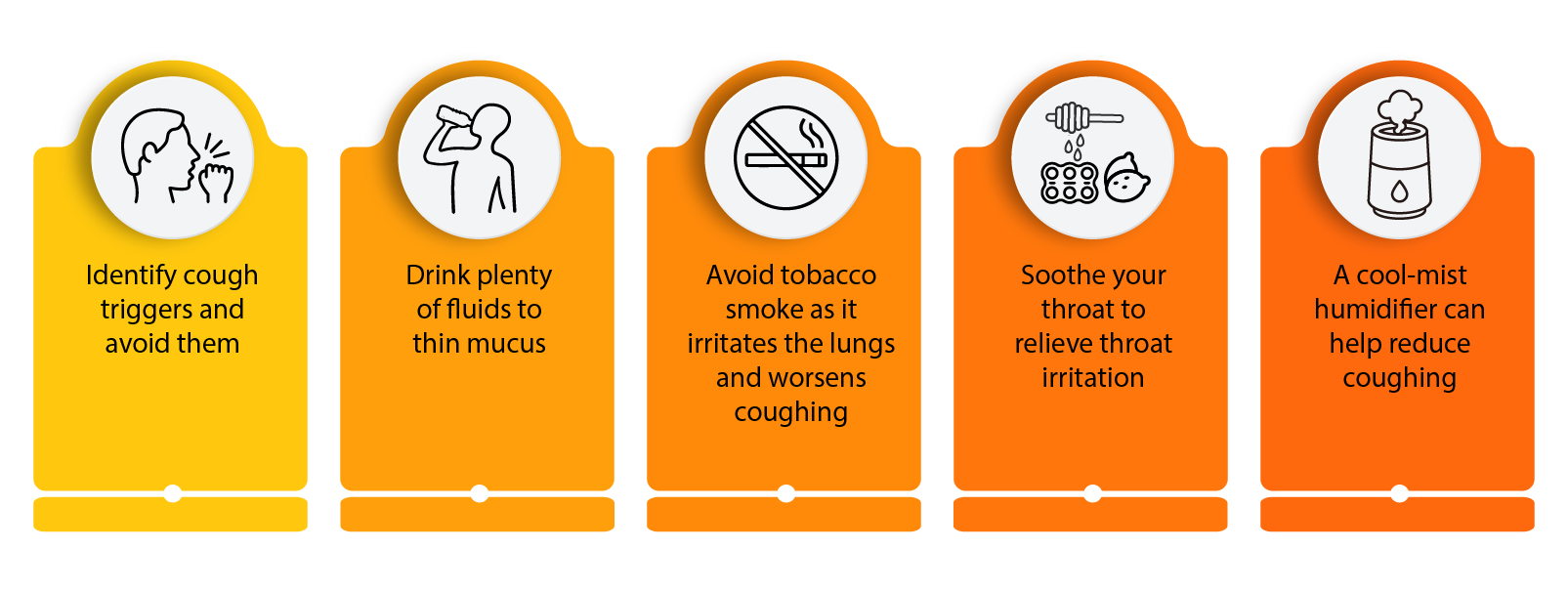
Managing Cough: Key Remedies
Management of Cough
Acute Cough Treatment:
- Empirical treatment: Most cases of acute cough should be treated empirically with a focus on symptomatic relief.
- Supportive measures:
- Use over-the-counter cough and cold medicines for symptomatic relief, noting that many antihistamine-decongestant medications may offer no clinical benefit over placebo.
- Cough suppressants:
- Cough suppressants can lessen the cough by blunting the cough reflex.
- Expectorants:
- Used when excessive mucus secretions are the primary issue to enhance mucus clearance.
- Antibiotic therapy: Tailored to the pathogen, typically prolonged for chronic infections (3 to 6 weeks) as needed.

Chronic Cough Treatment
- Target underlying etiology: Focus on treating the root cause rather than merely suppressing the cough.
- Drug induced cough:
- Discontinue angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors if they are causing the cough; consider switching to an alternative medication.
- Reactive airway disease:
- Inhaled steroids or anticholinergic medications may be necessary.

Gastroesophageal Reflux Management
- Avoid triggers: Eliminate chocolate, caffeine, alcohol, and tobacco from your diet.
- Positional therapy: Elevate the head of the bed and avoid eating for several hours before bedtime.
- Medical therapy: Use a proton pump inhibitor at maximum dosing.

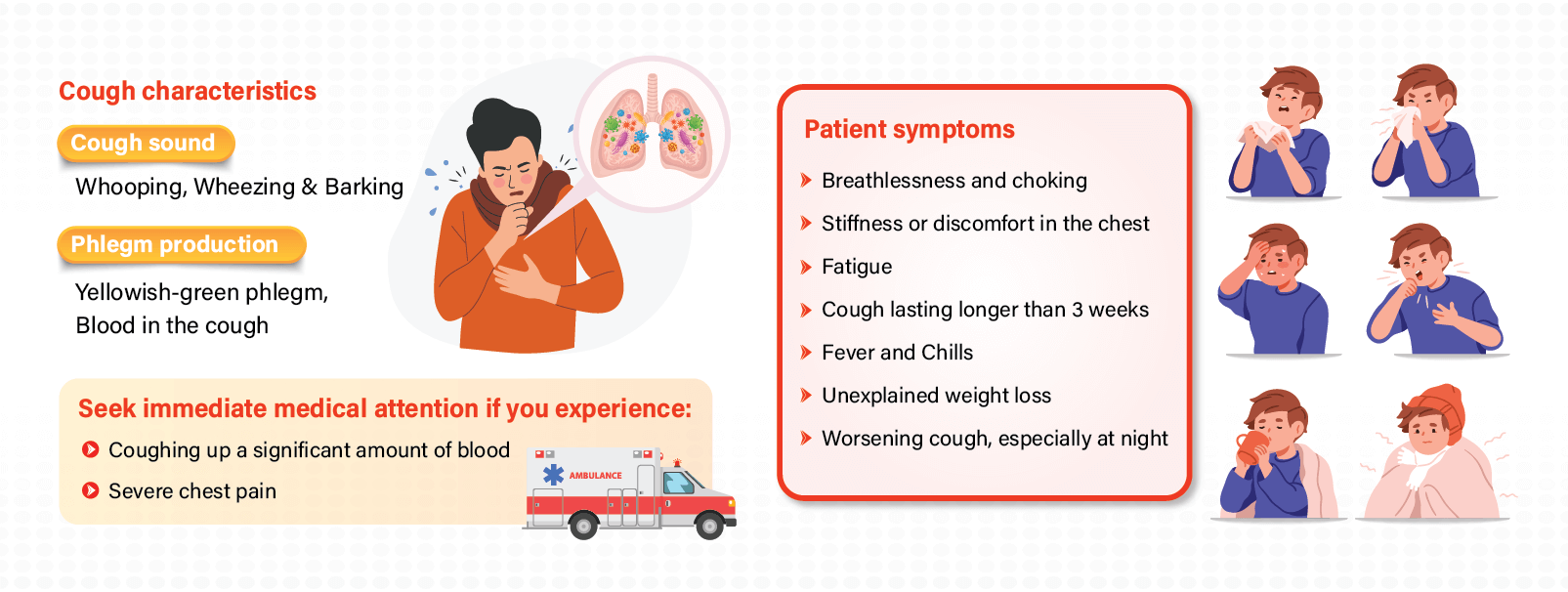
When should you worry about your cough?
Most coughs, especially those caused by colds and flu, go away fast. Coughs can, however, be caused by a variety of different conditions, some of the symptoms which may potentially indicate a bigger problem indicate a bigger problem necessitate medical treatment.